The olive tree or Olea Europea belongs to the Oleaceae family, which includes seventeen genera. It is a tree-like plant that is widespread throughout the world, especially in the range between the 30th and 45th parallels in the Northern Hemisphere and, to a lesser extent, in the corresponding warm-temperate range in the Southern Hemisphere.
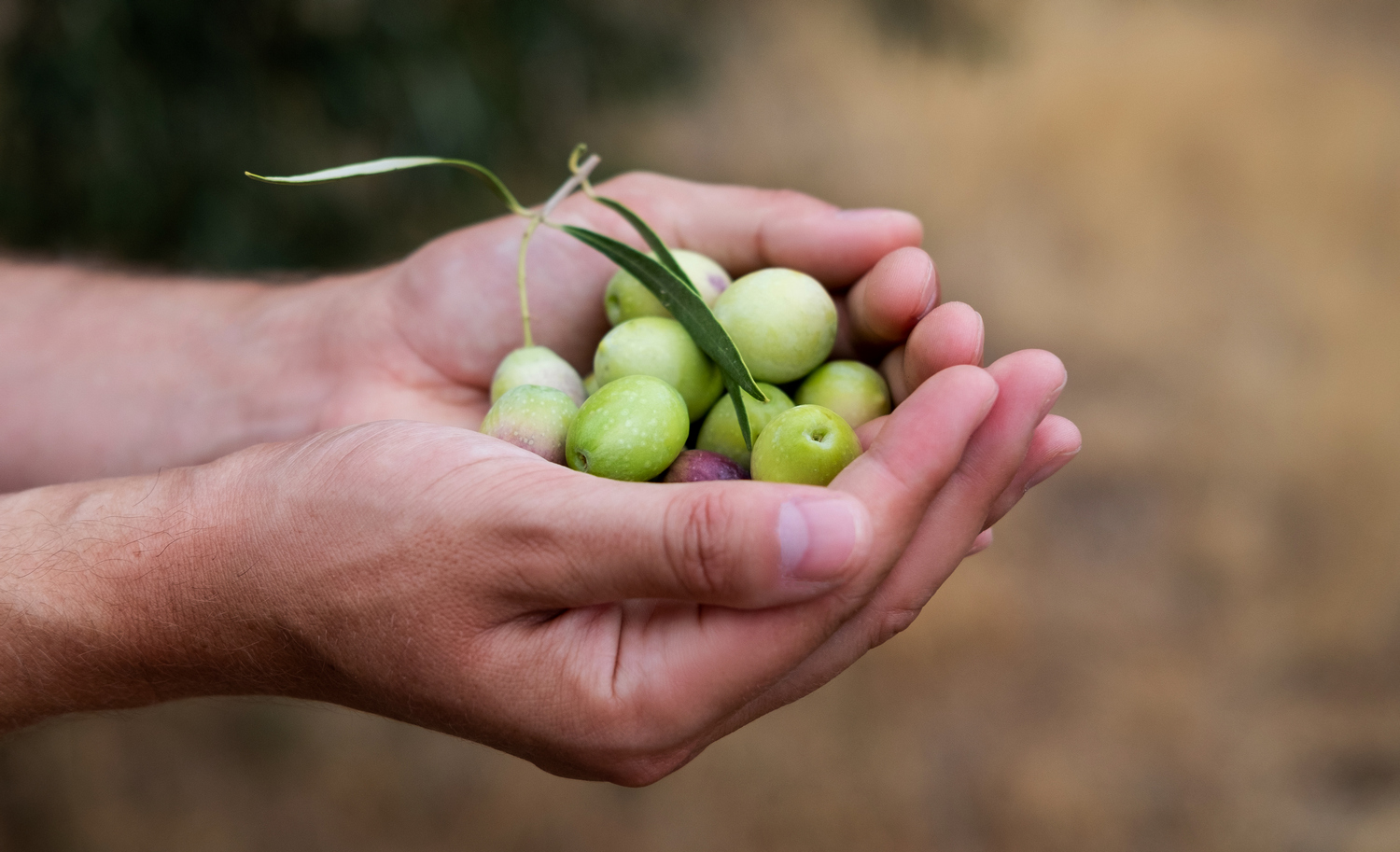

The olive tree's place of choice, first wild (oleaster) and then domestic, however, is the Mediterranean, and in particular the warm, dry coasts of this area. In fact, the olive tree needs a lot of sun and little water; it detests humidity and resists dryness.
Olea Europea is a fairly long-lived plant, reaching several hundred years. The tree is an evergreen, meaning that its vegetative phase is continuous throughout the year, with only a slight decline in the winter period. It is also a typically basitone species, meaning that it assumes a conical shape without the need for human intervention.

 Deutsch (Deutschland)
Deutsch (Deutschland)  English (United Kingdom)
English (United Kingdom) 